ANCIENT PHILOSOPHY
A History from the Presocratic Period through the Period of Schools
PHI 328: History of Ancient Philosophy
Thomas A. Blackson,
Philosophy Faculty
School of Historical, Philosophical, and Religious Studies
Arizona State University
Email: blackson@asu.edu
tomblackson.com
history-of-ancient-philosophy.com
www.public.asu/~blackson
These lectures notes and videos are works in progress.
INTRODUCTION
Ancient philosophy is the philosophical discussion that took place in Athens and other parts of the ancient Greek and Roman world in the period from 585 BCE to 529 CE.
A history of Ancient philosophy can be nothing more than a list of authors, their works, and brief descriptions of these works, but the goal is to do much more than that. It is to explain why Ancient philosophy came to exist and changed over time in the way it did.
In this course, we try to do this for parts of the first five hundred years of Ancient philosophy.
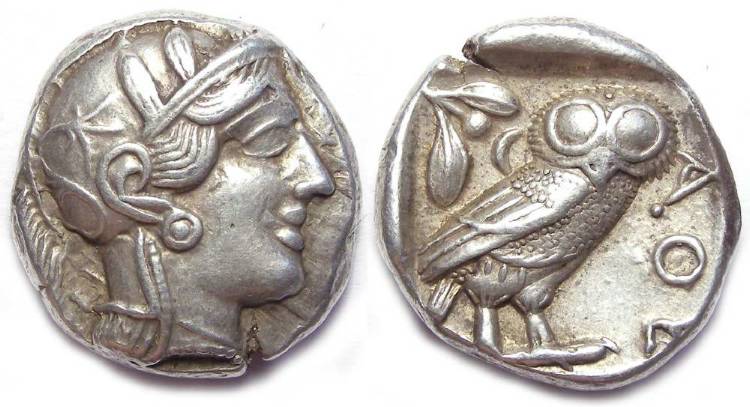

Athens, 5th century BCE. Silver tetradrachm
(τετράδραχμον).
Athena on the obverse. On the reverse, her sacred owl, an olive sprig, and
ΑΘΕ.
1 tetradrachm = 4 drachmas.
1 δραχμή
=
6 ὀβολοί
ΑΘΕ are the first letters of ΑΘΕΝΑΙΟΝ.
ΑΘΕΝΑΙΟΝ is written in "large letters" or majuscules. It is the older spelling of ΑΘΗΝΑΙΩΝ.
In minuscules, it is
Ἀθηναίων and means "[from the mint] of the Athenians."
The Latin
majusculus ("somewhat greater")
and
minusculus ("rather less")
gives us the words majuscule and minuscule.
Herodotus (5th century BCE Greek historian, born in Halicarnassus in Ionia in what is now Turkey) reports that the Lydians invented coins to facilitate trade.
"The customs of the Lydians are like those of the Greeks, except that
they make prostitutes of their female children.
They were the first men we know who coined and used gold and silver currency"
(Histories I.94).
Lydia was on trade routes that ran
west to the Aegean Sea, east to central Asia and southeast to Mesopotamia.
Course Outline
The Period and Method of Study
Some Online Resources
PRESOCRATICS
The Presocratic Period is the first of the three periods in Ancient Philosophy. In this period, a philosophical tradition comes to exist as a response to a need for a new kind of explanation.
THE BIRTH OF A PHILOSOPHICAL TRADITION
The Milesians Turn to Nature
Reason and Experience
The Tradition goes to Athens
SOCRATES
The Period of Schools is the second of the three periods in Ancient philosophy.
The first school in this period is the most famous. It is called the "Academy" (Ἀκαδημία). Plato founded it in about 387 BCE. He had been in the circle around Socrates. After the city of Athens executed Socrates in 399 BCE, Plato wrote dialogues about him.
Socrates himself left no written account of his thought. We depend on what others wrote about him. Several authors wrote about Socrates, but Plato is our primary source.
THE GOOD LIFE
The Focus on Socrates
Wisdom in the Soul
Understanding Socrates
AGAINST THE SOPHISTS AND RHETORS
The New Teachers
Teachings for the Soul
The Power of Rhetoric
PLATO
Plato's dialogues were transmitted from antiquity in their entirety. This is true of the work of no other philosopher in the Period of Schools. In his middle dialogues, Plato works through possible solutions to problems he uncovered in thinking about Socrates.
THREE PLATONIC THEORIES
Theory of Recollection
Theory of Forms
Theory of the Soul
JUSTICE AND ITS REWARD
Justice and the Good Life
What Justice Is
The Just Life is Happier
ARISTOTLE
Aristotle is the first great Platonist and Plato's first great critic. He accepts the broad framework of Plato's views, but he rejects and tries to correct what he regards as its excesses and mistakes.
Aristotle entered the Academy in 367 BCE (when he was in his teens) and remained until Plato's death in 347. In about 335, Aristotle founded his school. It is called the Lyceum.
For time considerations, I do not cover FIRST PHILOSOPHY in the class I teach for ASU.
SECOND PHILOSOPHY
The First Great Platonist
Sensible Substances
Teleology in Nature
PSYCHOLOGY
Souls are Forms
Theory of Induction
Becoming like God
FIRST PHILOSOPHY
Theory of Being
Substance Most of All
General Existence
ETHICS
The End of our Actions
Living like the Gods
Two Human Lives
HELLENISTIC PHILOSOPHERS
The Hellenistic philosophers belong to the Hellenistic Age. This is the time from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BCE to the end of the Roman Republic in 27 BCE.
In this time, Aristotle falls into the background. The focus in Plato's Academy returns to Socrates. Two new schools of philosophers emerge, the Epicureans and the Stoics.
REACTION TO THE CLASSICAL TRADITION
Epicurus and his School
Zeno and the Stoics
The New Academy
In about 100 BCE, the critical reaction that united the Hellenistic philosophers
was coming apart. This change traditionally marks the end of the Period of Schools.